5 usages of machine vision
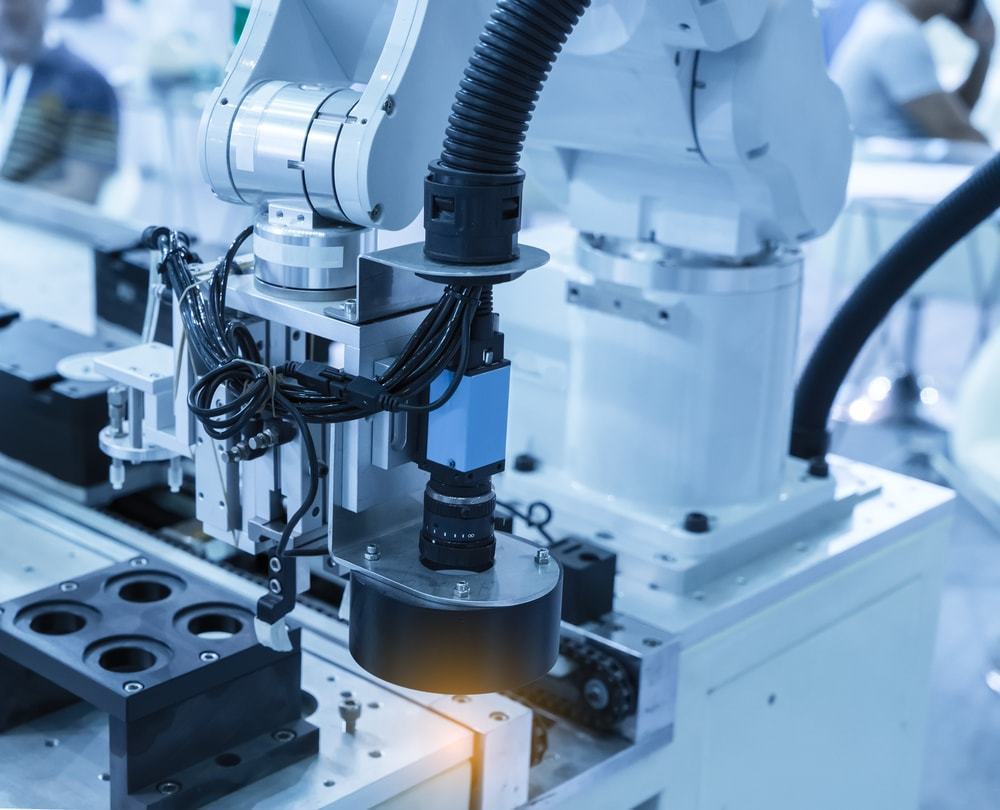
Machine vision is a paradigm and umbrella term for all industrial and non-industrial applications in which a combination of hardware and software provides operational guidance to devices in operations and functioning based on the capture and processing of images. Despite the fact that industrial computer vision uses many of the same algorithms and approaches as academic and military computer vision, the constraints are often very different.
In comparison to academic and research-oriented vision systems, industrial vision systems must be more robust, reliable, and stable. They are also typically less expensive than those used in military applications. As a result, industrial machine vision systems are typically low in cost, have acceptable accuracy, are extremely dependable and robust, and have high mechanical and temperature stability.
Machine Vision has exploded in popularity in recent years, especially in fast-paced industries like retail and manufacturing. These industries are using technology to improve the customer experience, optimise resource utilisation, and improve quality assurance.
- Supervision
In the manufacturing industry, guidance of machine vision companies has a wide range of applications. The majority of the time, it entails locating a specific part and ensuring proper placement and positioning to ensure that production runs smoothly with minimal errors and downtime. Machine vision can also be used to specify a part’s location and orientation. This data can then be passed on to a robot or machine controller for use in production.
- Documentation
To identify and categorise various products, machine vision techniques in identification applications mostly involve reading barcodes and data matrix codes. This is critical for ensuring that production and packaging processes are error-free. It’s also a lot faster and more precise than manual error proofing. By identifying bottlenecks in production pipelines, machine vision identification can also be used to improve productivity.
- Evaluating
Gauging by machine vision is a technique that is only used on production lines. A fixed-mount camera identifies two or more points on an object as it passes by on the production line in this application. If there is a discrepancy between the distances measured and the distances programmed into the vision system, the part is pushed off the line because it contains a manufacturing error. Machine vision guidance outperforms traditional methods like contact gauging in terms of speed and accuracy.
- Inspection & flaw recognition
Machine vision inspection, like gauging, is primarily used to detect flaws and defects. Machine vision inspection and flaw detection give you more options for inspecting a wide range of objects in a variety of industries, including agricultural products, textile flaws, prescription tablet branding marks, and more. Machine vision inspections are much faster and more accurate than manual inspection processes.
- Object recognition
Rather than looking at the entire image, the object detection algorithm looks for individual objects. Rather than classifying the entire image, the algorithm here is attempting to determine whether or not objects are present in the image. To perform efficient object detection, a variety of techniques are used. Object detection algorithms can be used in a variety of places throughout the manufacturing process, including quality control, inventory management, sorting, and assembly lines.








